State of Ruby 2026
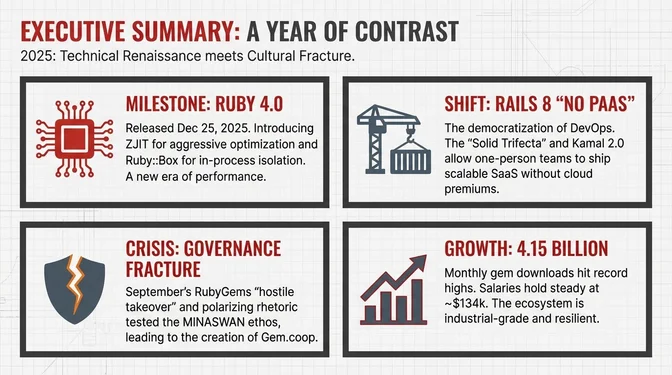
Ruby 4.0.0 launched on Christmas Day 2025, marking Ruby's 30th anniversary with two experimental features that signal the language's future direction: ZJIT (a new JIT compiler designed for aggressive optimization) and Ruby::Box (in-process isolation for definitions and loaded libraries). Rails 8.0 embraced a "No PaaS Required" philosophy with the Solid Trifecta (Solid Queue, Solid Cache, and Solid Cable), replacing Redis dependencies with database-backed alternatives, while Kamal 2.0 and Thruster simplified deployment to any Docker host. The community marked its milestone year with monthly RubyGems.org downloads surpassing 4 billion for the first time in April 2025 (4.15B), but a governance crisis over RubyGems control led to Yukihiro Matsumoto's (Matz) direct intervention, while polarizing statements from David Heinemeier Hansson (DHH) fractured the "MINASWAN" ethos.
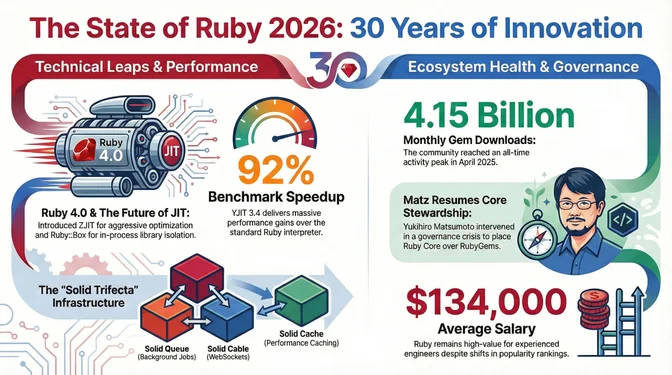
The tooling landscape improved across the board in 2025, with Shopify's Ruby LSP maturing rapidly as a full-featured IDE experience, Sorbet gaining RBS comments support for gradual type migration, and RubyMine 2025.3 integrating native AI assistants. Performance kept climbing as YJIT 3.4 posted major benchmark gains (production gains vary by workload), Hotwire continued to evolve with Turbo 8.x releases, and Puma 7.x reintroduced optimized keep-alive handling for high-concurrency workloads. Existing security infrastructure (MFA requirements for top gem maintainers and Trusted Publishing via OIDC; see Watchlist #4 for full details) faced a stress test when supply-chain attacks exposed 60+ malicious gems downloaded over 275,000 times since 2023. RubyGems responded by flagging and yanking offending packages and improving detection systems. The rise of AI coding agents created a "vibe shift": Rails' convention-over-configuration philosophy means many developers report AI tools work particularly well with Rails, and most professional developers now use AI assistants (84% are using or planning to use AI tools per Stack Overflow 2025; no Ruby-specific breakdown is available). Despite dropping to #24 on TIOBE (and GitHub Octoverse 2025 showing new repositories dominated by Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Java, C++, and C#), Shopify continues to invest heavily in Ruby infrastructure and GitHub's platform remains a Rails monolith with nearly two million lines of Ruby, while salaries average around $134,000 (ZipRecruiter, early 2026) and Rails jobs remain widely available in the US, the ecosystem prioritizes production stability over popularity metrics.
Actions for 2026: Upgrade to Ruby 3.4+ with YJIT enabled for immediate performance gains (Ruby 4.0's ZJIT is experimental; YJIT remains the production choice). Migrate from Redis to Solid Queue/Cache/Cable if running Rails 8+ to simplify infrastructure. Enable MFA on RubyGems.org and configure Trusted Publishing for your gems.
January 2025
YJIT 3.4 Performance Deep-Dive
Array#each rewritten in Ruby for better JIT optimization. Benchmarks showed 5-7% speedups over version 3.3.6.Ruby 3.3.7 Released
February 2025
net-imap Memory Exhaustion
Ruby 3.4.2 Released
Ruby Security Advisory Batch
March 2025
Sidekiq 8.0 Released
graphql-ruby Remote Code Execution
RubyGems.org New Security Policies
April 2025
Ruby Drops to TIOBE #24
RubyKaigi 2025 in Matsuyama
Ruby 3.5.0-preview1 Released
Sorbet Gains RBS Support
sig {} syntax to Ruby's official type annotation format.Rack Path Traversal Vulnerability
net-imap DoS Vulnerability
Record Gem Downloads
May 2025
Ecosystem Updates
June 2025
RedMonk Q1 Rankings Released
July 2025
resolv Gem DoS Vulnerability
RailsConf 2025 (Final Edition)
Bundler 2.7 Released
Stack Overflow 2025 Survey Results
August 2025
RubyMine 2025.2 Released
Supply Chain Attacks on RubyGems
Rails Security Patches
September 2025
Rails World 2025 in Amsterdam
RubyGems Governance Crisis Begins
"As I remember London"
TruffleRuby 25.0 Parallel Native Extensions
Security Updates
"The Ruby community has a DHH problem"
Mike Perham Withdraws Ruby Central Funding
DHH Responds to Critics
October 2025
gem.coop Mirror Launches
Puma 7.1.0 Released
Matz Intervenes in Governance Crisis
JetBrains Survey Results
Rails 8.1 Released
Ruby 3.3.10 and Security Fix
Governance Aftermath
Rails EOL Announcements
November 2025
Hanami 2.3.0 Released
Ruby 4.0 Previews
RubyGems 4.0.0 Betas
December 2025
RubyGems/Bundler 4.0
RubyMine 2025.3 Released
Ecosystem Updates
Performance/Detect well before 1.50.Ruby Website Redesign
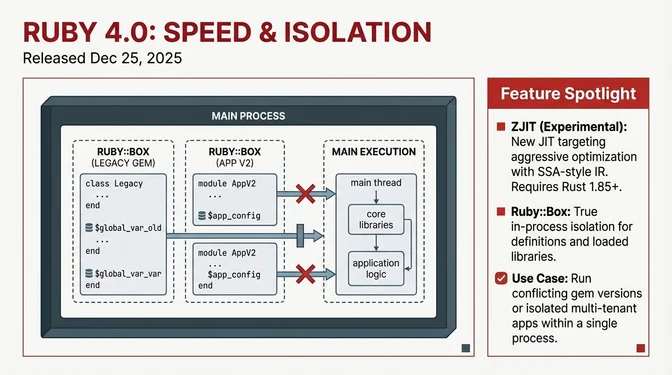
Ruby 4.0.0 Released
--zjit flag (requires Rust 1.85+). Faster than the interpreter but not yet as fast as YJIT on typical workloads, not yet production-ready, but designed to allow much more aggressive optimization long-term. The core team explicitly said "stay tuned for Ruby 4.1 ZJIT." ZJIT YouTube presentation by Takashi Kokubun provides deep technical context - Ruby::Box: In-process isolation of definitions and loaded libraries (opt-in via RUBY_BOX=1) creating segregated object spaces. Calling Ruby::Box.new creates a clean execution context. A gem loaded inside can patch core classes without changes leaking to other boxes. Useful for running different parts of a system (or even different gem versions) in the same process without them stepping on each other. Lays groundwork for a future high-level "package" system - Ractor improvements: New Ractor::Port class for safer message passing, reduced lock contention - Language changes: *nil no longer invokes nil.to_a, &&/|| allowed at line start as continuations - Core additions: Array#rfind, Set and Pathname promoted to core classes, --rjit support removedJanuary 2026
Resque 3.0.0 Released
Ruby 4.0.1 and TruffleRuby 33.0
Ruby 3.2.10 Released
Puma 7.2.0 Released
Rails 8.1.2 Released
Devise 5.0.0 Released
RuboCop 1.84.0 and Ruby 4.0 on Microsoft Store
Brakeman 8.0 Released
RubyConf Thailand and FOSDEM RubyGems Postmortem
JRuby 10.0.3.0 Released
gem.coop Cooldown Feature and Gem Fellowship Grants
37signals Open-Sources Fizzy
Community Governance (2025)
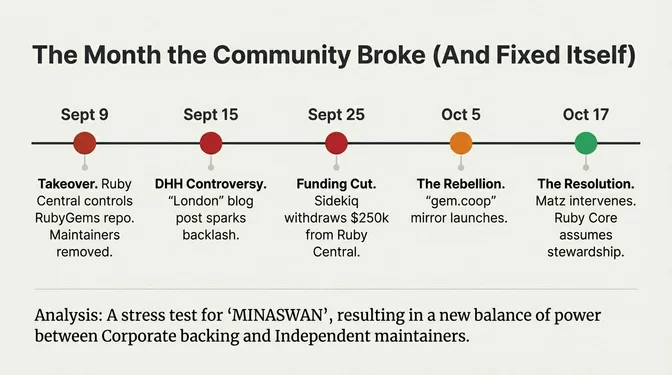
The Ruby community faced its most significant governance crisis in September 2025. Ruby Central secured funding from Shopify and restructured RubyGems/Bundler repository ownership on September 9 without maintainer consensus. Long-standing volunteers found their permissions revoked; Ellen Dash, a 10-year maintainer, called it a "hostile takeover" and resigned. Separately, Mike Perham withdrew a six-figure Sidekiq sponsorship (widely reported as about $250,000/year) from Ruby Central on September 25, citing objections to DHH's keynote at the final RailsConf in July. Matz intervened on October 17, placing Ruby Core as steward, while former maintainers launched gem.coop as an alternative mirror.
Simultaneously, DHH's polarizing blog posts sparked community backlash. The Plan Vert open letter, signed by Eugen Rochko (Mastodon), Tim Bray (XML co-author), and Jeff Atwood (Stack Overflow)—called for cutting ties with Rails' creator. No fork materialized, but the controversies split the community between "institutionalists" prioritizing corporate-backed stability and "independents" who saw these events as dangerous precedents for corporate capture.
Rails 8 and the Solid Stack
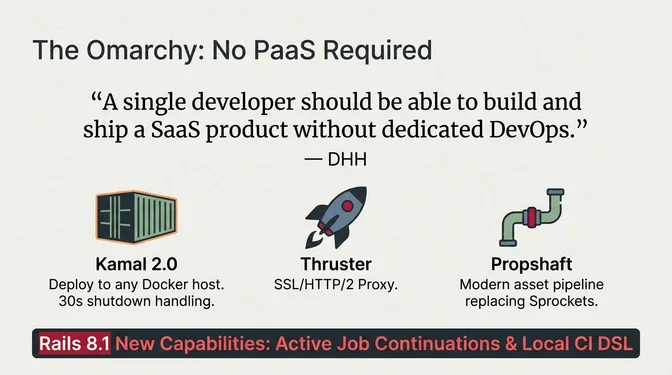
Rails 8.0 and 8.1 delivered on the Omarchy vision. Kamal 2 became the default deployment tool, Propshaft replaced Sprockets as the asset pipeline, and the Solid Trifecta eliminated Redis as a hard dependency: Solid Queue for background jobs, Solid Cache for caching, and Solid Cable for WebSockets, all database-backed via SQLite or Postgres.
Rails 8.1 introduced Active Job Continuations allowing long-running jobs to resume from checkpoints after interruption (critical for Kamal's 30-second container shutdown), plus native markdown rendering and a Local CI DSL. Hotwire continued to evolve with Turbo 8.x releases.
Performance Evolution
YJIT in Ruby 3.4 delivered significant speedups (see January timeline for benchmark details) through compressed metadata/context representation and improved register allocation. Ruby 3.3 optimized defined?(@ivar) with Object Shapes, and YJIT changes improved copy-on-write behavior for servers reforking with Pitchfork. Puma remained an HTTP/1.1 server with continued performance improvements through the 7.x series.
Ruby 4.0 introduced experimental ZJIT, a method-based JIT designed for aggressive optimization (not yet production-ready), and Ruby::Box for namespace isolation. Alternative implementations continued advancing: TruffleRuby 25.0 runs native extensions in parallel, JRuby 9.4 leverages JVM optimizations, and Artichoke compiles Ruby to WebAssembly.
Ruby 2026 Watchlist
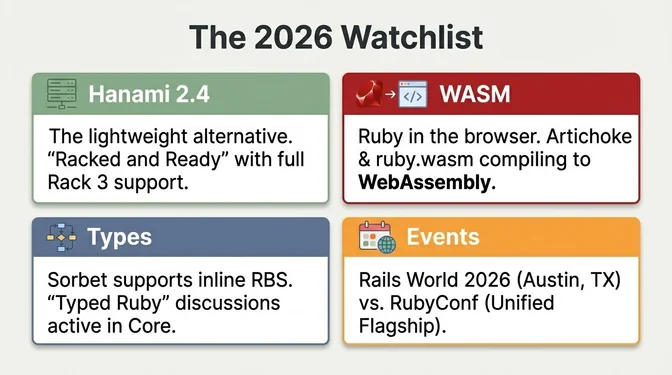
1. Ruby 4.1 and ZJIT Production Readiness
When: Late 2026 (timing TBD)
Context: ZJIT in Ruby 4.0 is experimental, faster than the interpreter but not yet as fast as YJIT. It targets larger compilation units and SSA-style IR, aiming for a higher long-term performance ceiling than YJIT's basic-block approach. Ruby 4.0.1 shipped January 13 as the first patch, with the core team confirming a 2-month release cadence. Ruby 4.1 may also remove Ractor's "experimental" tag, signaling production readiness for parallel execution.
Action: Track ZJIT benchmarks on the Rails at Scale blog. Test Ruby 4.0.1+ with ZJIT in non-production environments to prepare for 4.1 adoption.
2. Solid Trifecta Migration from Redis
When: Now
Context: Rails 8's Solid Queue, Solid Cache, and Solid Cable replace Redis with database-backed alternatives (SQLite for simplicity, Postgres/MySQL for scale), reducing infrastructure complexity. Solid Queue runs 20 million jobs per day for HEY, and Solid Cache is in production at Basecamp handling 10TB with 60-day retention, cutting P95 render times in half.
Action: Test Solid components on new Rails 8 projects. For existing applications, benchmark against current Redis usage before migrating.
3. RubyGems/Bundler Stewardship Resolution
When: Mid-2026
Context: Matz's intervention placed Ruby Core as steward, but the practical governance structure is still forming. gem.coop operates as an alternative mirror and added a cooldown feature in February 2026 allowing maintainers to delay gem releases for security review. A FOSDEM 2026 postmortem on January 31 detailed lessons learned from the September crisis and outlined the path forward under Ruby Core stewardship.
Action: Follow official Ruby announcements for the new RubyGems/Bundler core team structure. Consider whether your organization should mirror gems via gem.coop as backup infrastructure.
4. RubyGems MFA and Trusted Publishing
When: Now
Context: By mid-2025, RubyGems' MFA requirement (rolled out starting 2022) applied to owners of the top 100 gems and any gem with >180 million downloads. researchers found 60+ malicious gems in 2025 supply-chain attacks. Trusted Publishing (announced late 2023) via OIDC enables passwordless gem releases from CI. Work began on Sigstore integration for cryptographic signing of gems. RubyGems.org completed a security audit by Trail of Bits in late 2024, with Ruby Central reporting that it had begun fixing critical findings. Germany's Sovereign Tech Agency funded a third-party security review of Rails 8 features through OSTIF (with GitLab's help). Ruby Shield is Ruby Central's separate funding partnership with Shopify for Ruby infrastructure investment.
Action: Enable MFA on your RubyGems.org account immediately. Configure Trusted Publishing for gems published via GitHub Actions.
5. Rails World 2026 in Austin, Texas
When: September 2026
Context: Rails World has become the Rails Foundation's flagship event following RailsConf's discontinuation. The 2025 Amsterdam event drew 814 attendees from 62 countries and featured major announcements including Rails 8.1 beta.
Action: Watch for registration announcements in early 2026. Submit talk proposals if you have production Rails 8 experience to share.
6. RubyConf 2026 and Regional Events
When: Throughout 2026
Context: With RailsConf discontinued, RubyConf becomes Ruby Central's single flagship event with a dedicated Rails track. RubyKaigi 2026 runs April 22-24 in Hakodate, Hokkaido. RubyConf Thailand 2026 kicked off the year on January 31-February 1, drawing attendees from across Asia-Pacific. Other events include RubyConf AU 2026, Euruko 2026 (Warsaw), and Rails SaaS 2026. Ruby Central launched micro-grants for regional events and Rails Girls/RailsBridge workshops continue globally.
Action: Follow Ruby Central announcements for dates and CFP. Consider hosting or sponsoring local Ruby meetups through the micro-grant program.
7. Ruby::Box Namespace Isolation
When: Ongoing through 2026
Context: Ruby 4.0's experimental Ruby::Box provides in-process isolation of definitions and loaded libraries, particularly valuable for test isolation/parallelization and for running isolated web app boxes in parallel (for example, blue-green deployment and dependency-update evaluation). Watch for stabilization in Ruby 4.1.
Action: Experiment with Ruby::Box in isolated test environments. Watch the ruby-core mailing list for API stabilization announcements.
8. Shopify Ruby LSP Maturity
When: Now
Context: Ruby LSP reached version 0.26.x with full IDE feature parity including code completion, go-to definition, find references, and inline documentation. The ruby-lsp-rails and ruby-lsp-rspec extensions enable enhanced navigation and debugging. The debug gem, Ruby's bundled debugger since Ruby 3.1 (with features like record/replay), became the default in Rails 7; pry remains a separate REPL/debugging workflow. StandardRB provides opinionated zero-config linting/formatting. The irb-tools gem loads useful IRB extensions by default, and IRB gained experimental autocomplete using RBS or Sorbet types. A GitHub Actions RuboCop action became widely used, annotating pull requests with suggested fixes. Rails 7.1 and 8.x include built-in parallel testing using worker processes by default, with optional thread mode. As one developer noted: "With VSCode + Ruby LSP + Copilot, writing Rails code in 2025 feels like I have superpowers compared to 5 years ago."
Action: Install Ruby LSP in your editor. Add ruby-lsp-rails and ruby-lsp-rspec extensions for enhanced Rails development.
9. Type Annotation Convergence
When: Ongoing through 2026
Context: Sorbet now supports RBS inline comments, enabling gradual migration to Ruby's official type format. Large codebases (Shopify, Nx) run Sorbet, the Ruby static type checker by Stripe, though its momentum slowed after Stripe reorganized the Sorbet team in 2022, leading to interest in lighter-weight alternatives. Steep provides lightweight RBS type-checking and gained interest. There was talk at RubyKaigi of possibly integrating a gradual typing mode in a future Ruby version. A possible "Typed Ruby" mode with interpreter warnings on type violations is under discussion. If Ruby core signals moves toward types, 2026 could see an uptick in adoption.
Action: For Sorbet users, explore RBS migration path. For new projects, consider starting with RBS signatures and Steep for lighter-weight type checking.
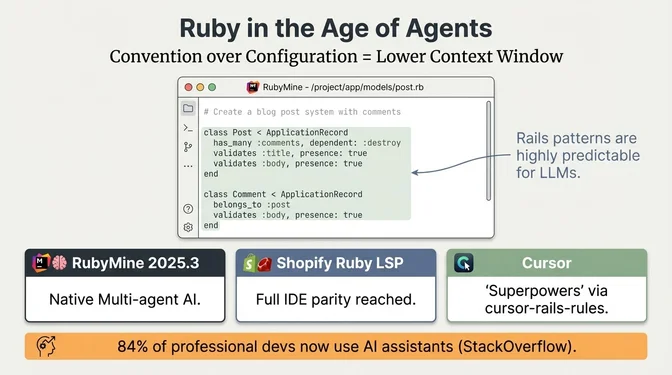
10. AI Coding Assistant Integration
When: Now
Context: Most professional developers now use AI assistants (84% are using or planning to use AI tools per Stack Overflow 2025; no Ruby-specific breakdown available). Rails' convention-over-configuration arguably means AI can generate features with fewer tokens and less context window usage than in more verbose frameworks. Cursor gained significant Rails adoption with community-maintained cursor-rails-rules. Shopify developed AI Dev Ex tools that can take a failing test and ask an LLM to explain what might be wrong. Gems like ruby-openai enable Rails apps to integrate AI features. One blogging platform added an "AI assist button" for authors using this pattern. A ChatGPT plugin for Ruby on Rails emerged that allows asking questions about your Rails app's codebase. For calling AI APIs, Ruby 3.2+'s async Fiber scheduler allows writing non-blocking HTTP calls easily, and the new Faraday-nethttp gem achieves better throughput for parallel requests via Fibers.
Action: Configure your AI assistant with Rails-specific rules. Try cursor-rails-rules for Cursor or explore RubyMine 2025.3's built-in AI assistants.
11. Hanami 2.4
When: 2026
Context: With Hanami 2.2 shipped in 2024 and 2.3 in November 2025, the next milestone is Hanami 2.4. The framework continues development as a lighter Rails alternative focused on performance and modularity, a good fit for developers who prefer explicit architecture over Rails' conventions.
Action: Try Hanami for new projects where Rails' conventions feel excessive. Watch the Hanami blog for 2.4 release announcements.
12. WebAssembly (WASM) Support
When: Ongoing
Context: There's growing interest in compiling Ruby to WASM. ruby.wasm (the official CRuby WebAssembly port under the Ruby organization) exists, and Artichoke (Ruby in Rust) can compile to WebAssembly. An official WASM build could allow Ruby scripts to run in browsers or Cloudflare Workers.
Action: Watch ruby-core discussions for official WASM support. Experiment with Artichoke for WebAssembly use cases.
13. Performance: YJIT and TruffleRuby
When: Now
Context: YJIT 3.4 is ~92% faster than the Ruby interpreter on Shopify's x86-64 benchmark suite; production gains are smaller and workload-dependent. Ruby 4.0 release notes state ZJIT is generally faster than the interpreter but does not yet match YJIT. Shopify reported Ruby 3.3 GC improvements including 33% and 19% reductions in average GC time per request from two GC changes. TruffleRuby 33.0 (January 2026) adopted simplified versioning and eliminated system dependency requirements, building on 25.0's ability to run native extensions in parallel. JRuby 10.0.3.0 (February 2026) continued improving Ruby 3.x compatibility on the JVM.
Action: Enable YJIT in production (--yjit flag or RUBY_YJIT_ENABLE=1). Try TruffleRuby for parallel-heavy workloads.
14. Job Market Dynamics
When: Ongoing
Context: Despite survey ranking declines, Ruby developer salaries average around $134,000 (ZipRecruiter, early 2026; aggregator estimate; actual ranges vary) and Rails jobs remain widely available in the US, concentrated in fintech, SaaS, and e-commerce with a shortage of senior engineers. Monterail's analysis found demand "largely stable" with tens of thousands of positions globally.
Shopify continues investing in YJIT and Sorbet rather than rewriting, and GitHub's platform remains a Rails monolith using techniques like backgroundable IO for performance. Migration trends show some companies introducing Kotlin/Go microservices, but counter-trends emerged: a startup wrote about switching from Node.js services back to Rails 7 and saw developer happiness improve. The big question: will Ruby's decline in rankings reverse or stabilize due to renewed interest from Rails 8+ and Ruby 4? The 2026 Stack Overflow survey will be telling. Ruby might slip a bit more unless the influx of new devs increases. But demand for experienced Ruby devs likely stays high, possibly even increasing if fewer people enter the field.
Action: For job seekers, emphasize Ruby/Rails expertise in fintech, SaaS, and e-commerce sectors. For hiring managers, expect competition for senior Ruby talent and consider upskilling junior developers.
15. Community Health and Events
When: Ongoing
Context: Ruby Central pivoted to supporting local and regional events with a micro-grant program. Regional conferences like RubyKaigi (Japan), Rails SaaS (virtual), RubyConf AU, and RailsConf Taiwan had strong attendance. The 2026 Gem Fellowship program announced $100,000 in grants for open-source Ruby infrastructure maintainers, providing direct funding for the ecosystem's critical dependencies. The Rails Foundation, launched in 2022 by Core members including Shopify and GitHub, funds Rails ecosystem work such as documentation, education, events, and marketing; Shopify maintains Ruby LSP. The Ruby Association in Japan continues its annual grant program. Initiatives like Rails Girls and RailsBridge workshops persist globally. The Foundation plans a guides.rubyonrails.org revamp for 2026, and the Foundation has signaled interest in funding junior developer outreach, possibly a Rails Fellowship or grants.
Action: Consider hosting or sponsoring local Ruby meetups. Apply for Ruby Association grants for Ruby projects. Volunteer with Rails Girls or RailsBridge workshops.
16. Beyond Rails: Alternative Ruby Frameworks and Libraries
When: 2026
Context: Beyond Hanami (see Watchlist #11), Bridgetown is gaining traction as a Ruby-based JAMstack static site generator. 37signals open-sourced Fizzy in February 2026, a lightweight full-text search library for Rails backed by SQLite, continuing the Solid Trifecta philosophy of reducing external dependencies. Dry-rb and ROM continue pushing Ruby's functional and data library capabilities. Package security is evolving; watch for possible signed gems and eventual 2FA requirements for all gem pushes.
Action: Consider Bridgetown for static sites and Fizzy for SQLite-backed search. Explore Dry-rb for domain logic that benefits from functional patterns.