State of Rust 2026
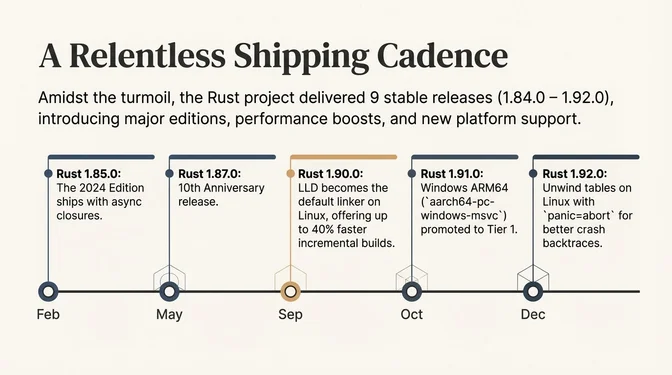
Two milestones bookended Rust's 2025: Rust 1.85.0 shipped the 2024 Edition in February with async closures and lifetime capture fixes, and in December the Linux kernel maintainers declared Rust "no longer experimental". Between these events, a Microsoft Distinguished Engineer set a goal to remove all C/C++ by 2030, Google reported ~1000x lower memory-safety vulnerability density in Android's Rust vs C/C++ code, and Ubuntu made sudo-rs the default in 25.10.
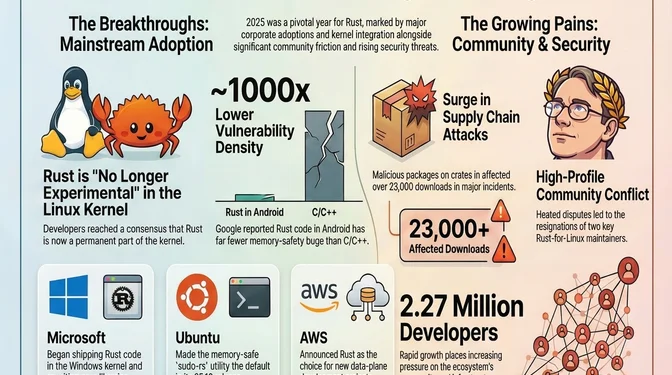
The year tested community resilience. The Rust-for-Linux project faced its second major resignation in six months when Hector Martin resigned from Asahi Linux after a heated mailing list exchange with Linus Torvalds over "social media brigading", following Wedson Almeida Filho's August 2024 departure over "nontechnical nonsense". Supply chain attacks hit crates.io repeatedly: typosquatting malware and OS-specific payloads in Web3 crates affecting 23,000+ downloads across the two largest incidents, plus a later exfiltration attempt and phishing campaigns targeting crate publishers. The Rust Foundation Maintainers Fund announcement prompted questions over undisclosed fund size and eligibility details. Through it all, Rust shipped 9 feature (.0) releases (1.84.0–1.92.0), crossed 2.27 million developers per JetBrains, and remained the most admired language in Stack Overflow's 2025 survey, every year since 1.0 in 2015. Behind the scenes, the Rust Foundation's infrastructure work kept releases flowing: 75% CI cost reduction, out-of-band daily backups for critical assets, and a full-time project manager.
Actions for 2026: Migrate to the Rust 2024 Edition, enable Trusted Publishing on crates.io, and review the LLD linker for faster builds on Linux.
January 2025
Axum 0.8.0
Rust 1.84.0
wasm32-wasi removed in favor of wasm32-wasip1/wasm32-wasip2.Rust DMA Patch Blocked
February 2025
Rust-for-Linux Governance Crisis
crates.io Development Update
Hector Martin Resigns as Kernel Maintainer
2024 State of Rust Survey Results
Hector Martin Resigns from Asahi Linux
Rust 1.85.0 and 2024 Edition
async || {}), #[diagnostic::do_not_recommend], improved RPIT lifetime capture, unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn warns by default.esp-hal 1.0.0-beta.0
March 2025
async-std Discontinued
European Rust Conferences
Program Management Expansion
Ferrocene Language Specification Donated
April 2025
Rust 1.86.0
&dyn Trait → &dyn Supertrait) and get_disjoint_mut for slices/HashMap enabling safe simultaneous mutable access.Datadog Lambda Extension Case Study
crates.io Session Cookie Exposure
Rust Konf Türkiye
May 2025
RustWeek 2025
Rust 1.87.0
std::io::pipe(), safe architecture intrinsics.June 2025
Clippy Feature Freeze
2025H2 Project Goals
NSA/CISA Memory Safety Guidance
Rust 1.88.0
#[naked]) for interrupt handlers, and Cargo garbage collection.July 2025
Trusted Publishing Enabled
DARPA TRACTOR Award
rustwasm Org Sunset
August 2025
Rust 1.89.0
x86_64-apple-darwin Demoted to Tier 2
September 2025
LLD Linker Default Announced
Microsoft Windows Kernel Driver Support
crates.io Phishing Campaign
Rust 1.90.0
cargo publish --workspace).Malicious Crates Removed
Bevy 0.17
October 2025
Default Branch Rename Plan
docs.rs Target Changes
aarch64-apple-darwin and aarch64-unknown-linux-gnu by default, reflecting the ARM64 shift.Clippy Feature Freeze Retrospective
Rust 1.91.0
November 2025
Rust Foundation Maintainers Fund
Google Android Security Update
December 2025
Project Director Update
evm-units and uniswap-utils Malware
finch-rust and sha-rust Malware
musl 1.2.5 Update
AWS Rust Default for Data-Plane
Rust 1.92.0
!) lints deny-by-default, external LLVM baseline raised to 20, and unwind tables on Linux with panic=abort for better crash backtraces.Linux Kernel Declares Rust Permanent
Microsoft C/C++ Elimination Goal
Adoption Metrics (2025)

45% report non-trivial organizational Rust use: a 7 percentage point increase from 2023, per the 2024 State of Rust Survey.
2.27 million developers used Rust over the past 12 months, with 709,000 identifying it as their primary language, per JetBrains.
72% admiration rate: Rust has been Stack Overflow's "most admired" language every year since 1.0 in 2015, though down from 83% in 2024 (a sign of mainstream adoption friction), per the 2025 survey.
TIOBE Index: #13: Rust reached its all-time high position of #13 in January 2026.
216,000+ crates on crates.io, having served 559 million downloads in a single day (as of January 2026).
Corporate Adoption (2025)

Microsoft: "Year of Rust." Microsoft porting Win32k graphics code to Rust, with GDI region code already shipping. SymCrypt cryptographic library rewrite in progress with formal verification. Hyperlight VM startup in 1–2ms. A Distinguished Engineer set a personal goal to remove all C/C++ by 2030 (a research project, not official company policy).
Google: ~1000x lower vulnerability density. Android's Rust code shows ~1000x lower memory-safety vulnerability density than its C/C++ code, with 4x lower rollback rates and 25% less code review time. Android's 6.12 kernel shipped Google's first production Rust driver.
AWS: Rust as default for data-plane projects. At re:Invent, AWS engineers discussed significant performance improvements from Rust migrations.
Linux Kernel: Rust "no longer experimental." At the December 2025 Maintainer Summit, developers concluded Rust's experimental phase ended; it's here to stay.
Ubuntu: sudo-rs default in 25.10. Questing Quokka released with the memory-safe sudo replacement as default.
Cloudflare: Pingora. Their Rust-based proxy framework open-sourced on GitHub.
Rust 2026 Watchlist

1. Rust 2024 Edition Migration
When: Now. Edition stable since February 2025.
Context: The Rust 2024 Edition brings async closures, improved lifetime capture for impl Trait, unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn warnings, and Cargo Resolver v3. Crates compile across editions, so migration is low-risk.
Action: Run cargo fix --edition to migrate. Update Cargo.toml to edition = "2024". Test async code for lifetime capture behavior changes.
2. crates.io Supply Chain Security
When: Now. Trusted Publishing available since July 2025.
Context: Three malware incidents plus a phishing campaign hit crates.io in 2025, including typosquatting and Web3-themed packages. Rust's memory safety doesn't protect against supply chain attacks, and the ecosystem is now a high-value target.
Action: Enable Trusted Publishing for all crates (OIDC from CI, no long-lived tokens). Audit dependencies with cargo audit and `cargo vet`. Pin versions with checksums in Cargo.lock. Review crate publishers before adding dependencies.
3. TUF (The Update Framework) for Supply Chain
When: Experimental deployment expected 2026.
Context: The Rust Foundation's 2025 review notes consensus on adopting TUF for Rust releases and crates.io, with an experimental out-of-tree deployment starting in 2026. TUF provides cryptographic verification of package integrity and protects against supply chain attacks including compromised mirrors and rollback attacks.
Action: Track Foundation announcements for TUF rollout timeline. For high-security environments, review signing and verification requirements now.
4. Rust ↔ C++ Interoperability
When: Ongoing. Foundation interop initiative active since 2025.
Context: The Rust Foundation joined WG21 (C++ standards committee) and is authoring/co-authoring proposals for safer interop. Key development: BorrowSanitizer funding to detect memory-safety violations at unsafe Rust/C++ boundaries, critical for incremental adoption in existing C++ codebases.
Action: For teams mixing Rust and C++ code: track BorrowSanitizer development for integration into CI pipelines. Track cxx and bindgen updates for interop ergonomics.
5. musl 1.2.5 Target Update
When: January 2026. Rust 1.93 (scheduled January 22, 2026).
Context: Linux musl targets updating to musl 1.2.5 includes resolver fixes but introduces a breaking change that can surface as linker errors (often undefined reference to open64) for projects with stale transitive dependencies.
Action: Before upgrading to Rust 1.93: run cargo update to refresh dependencies. If you encounter linker errors, check for crates with outdated C library assumptions. Alpine Linux and other musl-based systems are most affected.
6. Linux Kernel Rust Drivers
When: Ongoing.
Context: Rust is no longer experimental in the kernel. Android's 6.12 kernel shipped Google's first production Rust driver. The first CVE assigned to Rust code in the kernel (CVE-2025-68260) fixed a race condition in rust_binder that could lead to crashes (DoS). (Phoronix coverage)
Action: For kernel driver development: track Rust-for-Linux for stable APIs. Expect Rust-capable toolchain requirements in kernel builds.
7. LLD Linker Default
When: Now. Default on x86_64 Linux since Rust 1.90.0 (September 2025).
Context: LLD is faster than GNU ld. Benchmarks show up to 40% faster incremental builds and ~20% faster full debug builds. Critical for browser engines, kernel development, and large monorepos.
Action: Verify builds work with LLD. For other platforms, enable manually with -C link-arg=-fuse-ld=lld or [target.*.linker] in config.
8. Windows ARM64 Support
When: Now. Tier 1 since Rust 1.91.0 (October 2025).
Context: aarch64-pc-windows-msvc promotion guarantees Rust's full test suite runs on Windows ARM. ARM-based Surface devices and broader industry shift make this production-ready.
Action: Test Windows ARM64 builds for cross-platform applications. Update CI matrices to include ARM64 Windows targets.
9. Async Ecosystem Consolidation
When: Review in 2026. async-std discontinued March 2025.
Context: Tokio dominates the async runtime ecosystem. smol recommended for async-std users. Axum 0.8 removed the async_trait need. New ORMs: Toasty (Tokio team), Diesel 2.3 (security reviewed).
Action: Migrate from async-std to Tokio or smol. Review Axum 0.8+ for web services. Plan for TokioConf 2026 (April, Portland).
10. WebAssembly Target Migration
When: Now. wasm32-wasi removed in Rust 1.84.0 (January 2025).
Context: WASI targets split into wasm32-wasip1 (Tier 2) and wasm32-wasip2 (Tier 3). WASIp3 with native async support in development. wasm-bindgen transferred to new maintainers.
Action: Update target triples from wasm32-wasi to wasm32-wasip1. Track WASIp3 for async workloads.
11. Embedded Rust Production Readiness
When: Now. esp-hal 1.0.0-beta.0 released February 2025.
Context: First vendor-backed embedded Rust SDK (Espressif). Embassy runs on stable Rust (MSRV 1.75) with HALs for 1400+ STM32 chips, Nordic nRF, RP2040/RP23xx. embedded-hal 1.0 stable.
Action: Review esp-hal for ESP32 projects. Consider Embassy for async embedded. Expect more vendor investment in Rust embedded toolchains.
12. Safety-Critical Rust
When: Ongoing. Consortium active since 2024.
Context: The Safety-Critical Rust Consortium continues work on tooling and processes for Rust in IEC 61508 (functional safety), ISO 26262 (automotive), and DO-178C (aviation) environments. Ferrocene, the first qualified Rust toolchain, donated its Language Specification to the Rust Project in March 2025.
Action: For safety-critical domains: track Consortium announcements. Review Ferrocene for projects requiring qualified toolchains. Track language specification work (RFC 3355) for compliance documentation.
13. Rust Foundation Training & Accreditation
When: More details expected Q1 2026.
Context: The December 2025 Project Director Update notes a member-company listening session on the Foundation's training course and accreditation program, with more to come in Q1 2026. This addresses employer demand for verifiable Rust competency.
Action: Track Foundation announcements for training program details. Organizations hiring Rust developers: review accreditation as a hiring signal once available.
14. Maintainer Sustainability
When: Critical in 2026. Maintainers Fund announced November 2025.
Context: Employers pay many Rust contributors to work on Rust full-time. The "tragedy of the commons" in open source intensifies as Rust becomes critical infrastructure.
Action: Organizations using Rust commercially: consider Rust Foundation membership or direct contributor sponsorship via GitHub Sponsors for Rust contributors.
15. 2026 Project Goals (Annual Cadence)
When: Draft slate January, RFC March, announce April 2026.
Context: The Goals team formalized the shift to annual goals with quarterly check-ins. This replaces the six-month cycle and provides clearer planning for contributors and consumers.
Action: If you have a proposal for the 2026 cycle, reach out to the Goals team by January. Track the RFC in March for what the project will focus on.
16. RustConf 2026
When: September 8-11, 2026.
Context: RustConf 2026 in Montreal. First conference in Canada.
Action: Track CFP announcements for submission deadlines.