State of TypeScript 2026
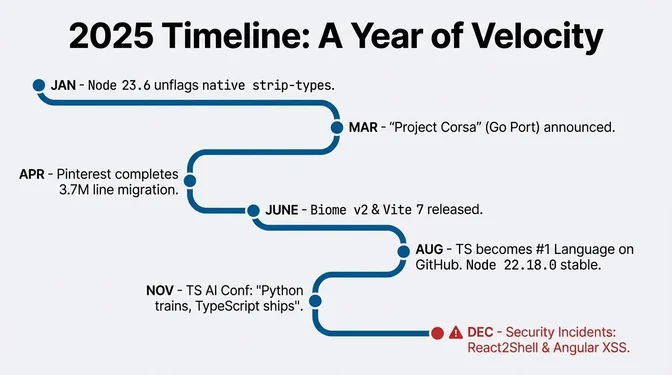
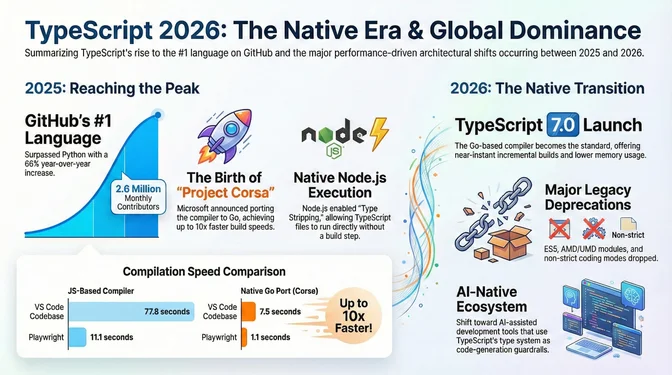
2025 marked a turning point for TypeScript's role in the JavaScript ecosystem, with TypeScript becoming GitHub's #1 language by contributor count. In August 2025, TypeScript became the most-used language on GitHub with 2,636,006 monthly contributors (+66% YoY), which GitHub called "the most significant language shift in more than a decade." Earlier in the year, Microsoft announced "Project Corsa", a native port of the TypeScript compiler and language service to Go, targeting ~10x faster builds and major editor responsiveness gains. Initial benchmarks showed the VS Code codebase compiling in 7.5 seconds versus 77.8 seconds, while Playwright dropped from 11.1s to just 1.1s. The JavaScript-based toolchain continues through TypeScript 6.0.x as the ecosystem transitions; Microsoft plans TypeScript 6.0 as the last JS-based major release.
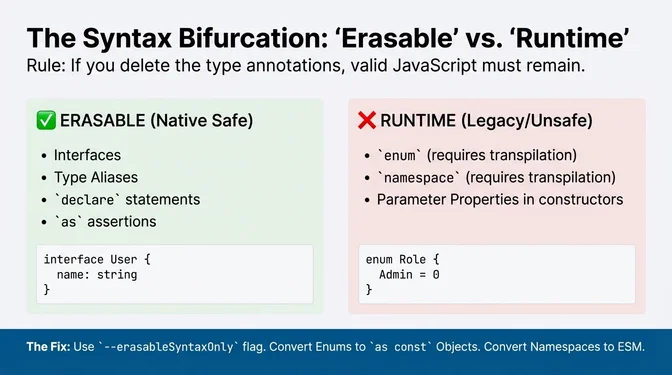
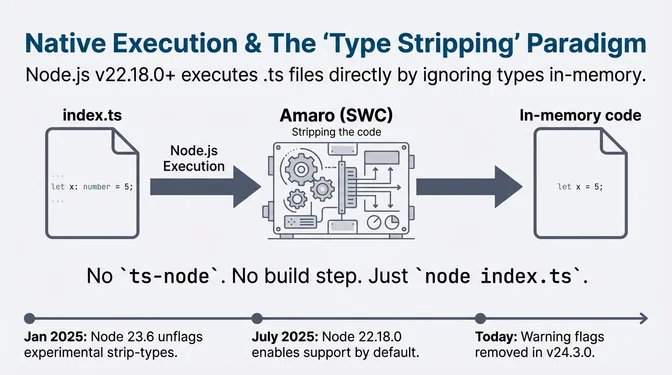
Simultaneously, the runtime environment underwent radical simplification. Node.js 23.6 and 22.18 enabled native TypeScript execution via "Type Stripping" by default, a feature that fundamentally bifurcated the language into "erasable" syntax (types, interfaces) and "runtime" syntax (enums, namespaces). By July 31, Node.js 22.18.0 enabled type stripping by default, Node removed warnings in v24.3.0/22.18.0, and later stabilized the feature in v25.2.0. Yet, this maturation occurred against a backdrop of severe security instability. The ecosystem faced sophisticated, automated threats across npm compromises in 2025, alongside critical serialization vulnerabilities in frameworks like Next.js, such as the "React2Shell" RCE (CVE-2025-55182), a CVSS 10.0 vulnerability forcing a reevaluation of security models governing full-stack JavaScript.
Actions for 2026: Audit npm dependencies affected by 2025 compromises and require publish-time 2FA plus granular tokens for maintainers where possible; enable --erasableSyntaxOnly to prepare codebases for Node.js native TypeScript execution; migrate enums to as const objects and namespaces to ES modules before adopting erasableSyntaxOnly / Node type stripping workflows; test TypeScript 7.0 preview (@typescript/native-preview) on CI pipelines to benchmark 10x compilation speedups; patch React/Next.js applications against CVE-2025-55182 and related RSC vulnerabilities; review Biome v2 for type-aware linting with lower runtime overhead; plan migration strategy for TypeScript 6.0 planned deprecations and defaults under consideration (e.g., strict-by-default, automatic @types inclusion disabled).
January 2025
Node.js 23.6 Unflagged
--experimental-strip-types option, enabling direct execution of TypeScript files without external loaders like ts-node or tsx. This feature, powered by the SWC-based Amaro library, removed the need for a build step in Node.js core for the first time.TypeScript 5.8 Beta
--erasableSyntaxOnly flag to align with Node.js's experimental type-stripping mode. This beta introduced checked return types for conditional/indexed access types.February 2025
TypeScript 5.8 GA
require() support for ESM under --module nodenext. The --erasableSyntaxOnly compiler option generates errors for features requiring runtime transpilation (specifically enums, namespaces, and parameter properties), marking them as incompatible with erasable-only execution. The team pulled back conditional return type checking to iterate further for version 5.9.TypeScript La Conf
March 2025
Project Corsa Unveiled
April 2025
Records & Tuples Withdrawn
Pinterest Migration Complete
May 2025
TypeScript Native Previews
@typescript/native-preview, providing a tsgo executable alongside a VS Code extension.Angular 20.0.0
June 2025
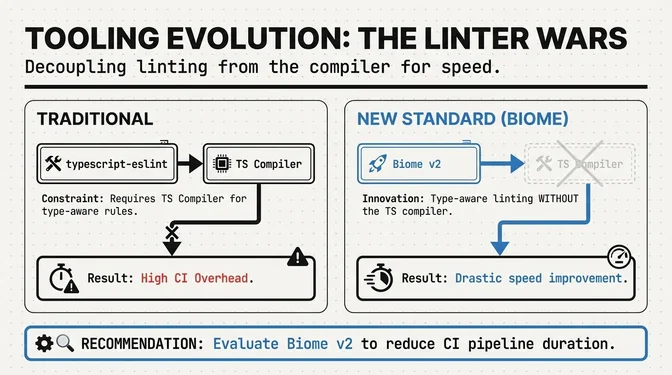
Biome v2 Launched
Vite 7 Released
buildApp hook.July 2025
TypeScript 5.9 Beta
import defer proposal for lazy module evaluation.Node.js 22.18.0
node file.ts without a separate compile step, though type checking still requires running tsc.August 2025
TypeScript 5.9 Stable
tsc --init generating minimal best-practice configuration, support for --module node20, editor improvements with expandable hovers, and performance tweaks for huge union types. TypeScript #1 on GitHub
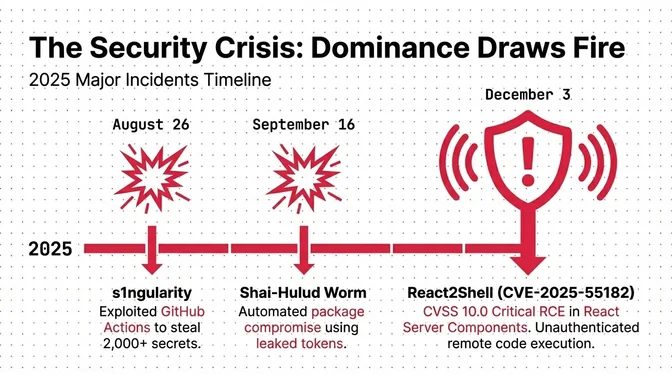
s1ngularity Attack
pull_request_target workflow), stealing credentials and publishing infected packages, with over 2,000 secrets/tokens leaked.September 2025
debug/chalk Compromise
Shai-Hulud Worm
October 2025
React 19.2
<Activity> component for off-screen prioritization and useEffectEvent to solve dependency array pain points, aligning further with the concurrent rendering model.Octoverse 2025
November 2025
TypeScript AI Conference
Angular v21
December 2025
Angular XSS Patched
<svg><animate href="javascript:..."> patterns.TypeScript 7 Progress Update
React2Shell Disclosed
Compiler + Runtime Shift
Project Corsa moves the TypeScript compiler and language service to a Go port, targeting major performance and memory gains while signaling a disruptive toolchain transition. In parallel, Node’s type-stripping support enables direct .ts execution in core, and the `--erasableSyntaxOnly` flag formalizes a “just-JS-at-runtime” path that pushes enums/namespaces toward as const objects and ES modules. The new reality: faster compiles, but stricter runtime constraints and a migration path that favors erasable syntax.
Ecosystem, Frameworks, and Tooling
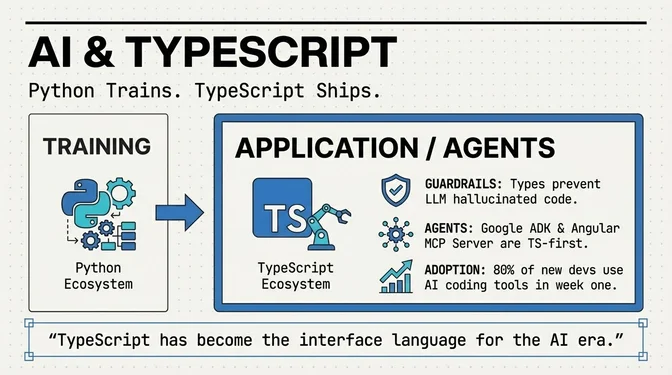
Default TS scaffolding across major frameworks reinforces TypeScript's dominance and continued enterprise adoption. Framework updates (React 19.2, Angular 21, Vite 7 and Vite 8 with Rolldown) move the ecosystem toward faster builds and more consistent runtimes, while tooling shifts toward type-aware linting without TypeScript’s compiler (Biome v2) and stronger IDE performance via the Go language service. AI integrations are now standard: Google ADK, Angular’s AI hub and MCP server, and IDE copilots that make TS the default interface for codegen.
Security and Supply Chain Pressure
The npm ecosystem saw a chain of incidents (s1ngularity, debug/chalk, Shai‑Hulud) that exposed systemic weaknesses in maintainer auth and CI workflows. Security responses now emphasize granular tokens, publish-time 2FA, and stricter release policies. On the app side, React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) and follow-on issues underscored the risks in RSC serialization, while Angular’s XSS and other runtime CVEs kept security upgrades at the top of 2025’s backlog.
Standards and Language Trajectory
TC39 withdrew Records & Tuples after the proposal failed to reach consensus, while Temporal began shipping in engines even as TypeScript’s standard libs still lack Temporal typings (track TypeScript issue #60164). The type-annotations proposal remains early-stage, but it frames the longer-term path: a JS runtime that can ignore type syntax while TS evolves as a superset. Combined with TypeScript 7's upcoming breaking changes and API shifts, the direction for standards is clear: consolidation, stricter defaults, and fewer "magic" features at runtime.
TypeScript 2026 Watchlist
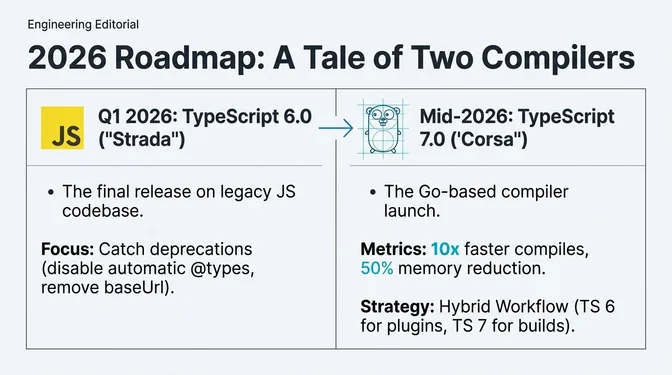
1. TypeScript 6.0 Release
When: Q1 2026 (RC possibly January, final by February/March)
Context: Last version on old compiler codebase ("Strada"), transitional release to prep ecosystem for 7.0 with planned deprecations and defaults under consideration.
Action: Enable --deprecation flag to identify deprecated features; plan migrations for --baseUrl, moduleResolution: node, non-strict mode, ES5 targeting.
2. TypeScript 7.0 Launch
When: Mid/Late 2026 (Summer anticipated)
Context: Go-based compiler ("Corsa") with 5-10x faster compiles, near-instant incremental builds, ~8x editor startup improvement, ~50% memory reduction.
Action: Test @typescript/native-preview on CI pipelines; audit third-party tools for Corsa API compatibility; prepare hybrid approach using tsc (6.x) for plugins and tsgo (7.0) for builds.
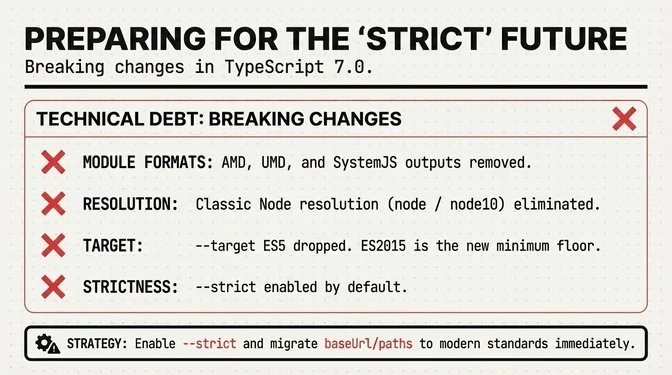
3. Breaking Changes Migration
When: Throughout 2026
Context: --strict on by default; --target ES5 dropped (ES2015+); AMD/UMD/SystemJS module outputs removed; classic Node module resolution (node/node10) removed; baseUrl gone.
Action: Use migration tools (ts5to6, ts6to7); update CI configurations; audit build pipelines for deprecated module formats.
4. Rolldown 1.0 Stabilization
When: H1 2026
Context: Rust-based bundler becoming default for entire Vite ecosystem (Nuxt, SvelteKit, Astro), effectively retiring esbuild and Rollup for millions of users.
Action: Test Vite 8 beta with Rolldown-powered builds; benchmark production build times; review "Full Bundle Mode".
5. Node.js 26 LTS
When: October 2026 (projected)
Context: Built-in TypeScript support fully stable; erasable syntax paradigm as default for new projects.
Action: Migrate development workflows to native TypeScript execution; remove ts-node/tsx dependencies where possible.
6. Type Annotations Proposal Advancement
When: Mid-2026 TC39 meetings
Context: Stage 1 proposal for native type syntax in JavaScript; if Stage 3, browsers might add experimentally.
Action: Track proposal progress; review impact on toolchain if browsers begin experimental implementation.
7. Framework Major Releases
When: Late 2026
Context: Angular 22 likely to raise TypeScript baseline; React 20 might migrate from Flow to TypeScript; Vue 4 potential new reactivity system.
Action: Track framework announcements at Google I/O and React Conf; plan framework upgrade timelines.
8. AI-Native Tooling Maturation
When: Throughout 2026
Context: First generation of frameworks designed specifically for code generation; TypeScript's type system as guardrails for AI-generated code.
Action: Review Google ADK, Mastra AI, VoltAgent for AI agent development; integrate AI-assisted tooling into development workflows.
9. ESLint/TypeScript-ESLint Major Version
When: H1 2026
Context: New major version to support TypeScript 7 API; possibly faster TypeScript-aware linter emerges.
Action: Track typescript-eslint compatibility with Corsa API; review Biome v2 as alternative.
10. Supply Chain Security Hardening
When: Ongoing
Context: Post-2025 incidents tightened npm auth: granular, short-lived tokens and broader publish-time 2FA enforcement defaults.
Action: Audit all npm dependencies; require publish-time 2FA and granular tokens where possible; add package lockfile verification; consider private registry mirrors for critical dependencies.